| Windows 8 | |
|---|---|
| Part of the Microsoft Windows family | |
 |
|
Windows 8 introduces significant changes to the operating system's platform, primarily focused towards improving its user experience on mobile devices such as tablets to rival other mobile operating systems (such as Android and iOS), taking advantage of new and emerging technologies (such as USB 3.0, UEFI firmware, near field communications, cloud computing, and the low-power ARM architecture), new security features (such as malware filtering, built-in antivirus software, and support for secure boot, a controversial UEFI feature which requires operating systems to be digitally signed to prevent malware from infecting the boot process), along with other changes and performance improvements.
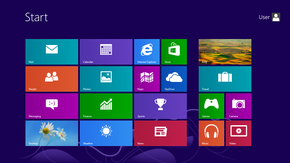
Windows 8 also introduces a new shell and user interface based on Microsoft's "Metro" design language, featuring a new Start screen with a grid of dynamically updating tiles to represent applications, a new app platform with an emphasis on touchscreen input, the new Windows Store to obtain and purchase applications for the system, and the ability to synchronize programs and settings between multiple devices.
Hardware requirements
PCs
| Architecture | IA-32 (32-bit) | x86-64 (64-bit) |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 1 GHz (with PAE, NX and SSE2 support) | |
| Memory (RAM) | 1 GB | 2 GB |
| Graphics Card | DirectX 9 graphics device with WDDM 1.0 or higher driver | |
| Storage | 16 GB | 20 GB |
To receive logo certification, Microsoft requires that an Intel-compatible system resume from standby in 2 seconds or less.
New features and functionality in Windows 8 include a faster startup through UEFI integration and the new "Hybrid Boot" mode (which hibernates the Windows kernel on shutdown to speed up the subsequent boot), a new lock screen with a clock and notifications, and the ability for enterprise users to create live USB versions of Windows (known as Windows To Go).[36][37] Windows 8 also adds native support for USB 3.0 devices, which allow for faster data transfers and improved power management with compatible devices, along with support for near field communication to facilitate sharing and communication between devices.New and changed features
Windows Explorer, which has been also renamed File Explorer, now includes a ribbon in place of the command bar. File operation dialogs have been updated to provide more detailed statistics, the ability to pause file transfers, and improvements in the ability to manage conflicts when copying files. A new "File History" function allows incremental revisions of files to be backed up to and restored from a secondary storage device, while Storage Spaces allows users to combine different sized hard disks into virtual drives and specify mirroring, parity, or no redundancy on a folder-by-folder basis.
Task Manager has also been redesigned, including a new processes tab with the option to display fewer or more details of running applications and background processes, a heat map using different colors indicating the level of resource usage, network and disk counters, grouping by process type (e.g. applications, background processes and Windows processes), friendly names for processes and a new option which allows to search the web to find information about obscure processes.Additionally, the Blue Screen of Death has been updated with a simpler and modern design with less technical information displayed.
Safety and security
Additional security features in Windows 8 include two new authentication methods tailored towards touchscreens (PIN numbers and picture passwords),, the addition of antivirus capabilities to Windows Defender (bringing it in parity with Microsoft's Security Essentials software) SmartScreen filtering integrated into the desktop, and support for the "Secure Boot" functionality on UEFI systems to protect against malware infecting the boot process. Parental controls are offered through the integrated Family Safety software, which allows parents to monitor and control their children's activities on a device with activity reports and safety controls. Windows 8 also provides integrated system recovery through the new "Refresh" and "Reset" functions.Online services and functionality
Windows 8 provides heavier integration with online services from Microsoft and others. A user can now log in to Windows with a Microsoft account, formally known as a Windows Live ID, which can be used to access services and synchronize applications and settings between devices. Windows 8 also ships with a client app for Microsoft's SkyDrive cloud storage service, which also allows apps to save files directly to SkyDrive. A SkyDrive client for the desktop and File Explorer is not included in Windows 8, and must be downloaded separately. Bundled multimedia apps are provided under the Xbox brand, including Xbox Music, Xbox Video, and the Xbox SmartGlass companion for use with an Xbox 360 console. Games can integrate into an Xbox Live hub app, which also allows users to view their profile and gamerscore. Other bundled apps provide the ability to link to services such as Flickr and Facebook.Internet Explorer 10 is included as both a desktop program and a touch-optimized app, and includes increased support for HTML5, CSS3, and hardware acceleration. The Internet Explorer app does not support plugins or ActiveX components, but includes a version of Adobe Flash Player that is optimized for touch and low power usage, but works only on sites included on a whitelist. The desktop version does not contain these limitations.
Windows 8 also incorporates improved support for mobile broadband; the operating system can now detect the insertion of a SIM card and automatically configure connection settings (including APNs and carrier branding), track and reduce bandwidth use on metered networks. Windows 8 also adds an integrated airplane mode setting to globally disable all wireless connectivity as well. Carriers can also offer account management systems through Windows Store apps, which can be automatically installed as a part of the connection process and offer usage statistics on their
Removed features
Main article: List of features removed in Windows 8
Aside from the removal of the Start menu, several notable features have been removed from Windows 8. Support for playing DVDs has been removed from Windows Media Player due to the cost of licensing the necessary decoders (especially for devices which do not include optical disc drives at all) and the prevalence of streaming services such as Netflix. For the same reasons, Windows Media Center
will no longer be included by default on Windows 8 as well, but the
software (which also includes support for DVD playback) can be added
back through the paid "Pro Pack" (for the base version of Windows 8,
which also upgrades the system to Windows 8 Pro) or "Media Center Pack"
(for Windows 8 Pro) add-ons. Windows 8 will still support third-party
DVD playback software.File History, the new backup feature of Windows 8 described above, replaces Backup and Restore, the former backup app, and Previous Versions, a component of Windows Explorer that saves previous versions of changed files. Backup and Restore is deprecated but will continue to work on preset schedule on computers that upgrade from Windows 7 to Windows 8. Previous Versions no longer protects local files, although it is still available to access previous versions of shared files stored on a Windows Server computer. Shadow Copy, the subsystem component based on which these worked, however, is still available for other software to use.
Windows 8 also removed the ability to customize the font color as well as the color of maximize/minimize buttons in the title bar which renders it almost impossible to read the text and see the buttons - in case the user chooses a dark color for the Windows borders and taskbar.




0 comments:
Post a Comment